Pomoč:IPA za angleščino
Videz
V Wikipediji je izgovorjava angleških besed posredovana s pomočjo Mednarodne fonetične abecede (IPA). (Če vaš spletno brskalnik nepravilno prikazuje IPA simbole, glejte povezave na dnu te strani.)
Ključ
[uredi | uredi kodo]Opomba: IPA naglasno znamenje (ˈ) se nahaja pred zlogom, ki vsebuje naglas, v nasprotju z označevanjem naglasov v nekaterih slovarjih izdanih v ZDA.

(Besede zapisane z MAJHNIMI VELIKIMI ČRKAMI so standardni leksikalen nabor angleških besed.)
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Glej tudi
[uredi | uredi kodo]- Če vaš brskalnik ne prikazuje IPA simbolov, morate verjetno instalirati font, ki vsebzuje IPA. Prosto dostopne IPA fonte vključuje Gentium in Charis SIL (popolnejši); monospaced font je Everson Mono, ki je popoln.
Opombe
[uredi | uredi kodo]- ↑ If the two characters ⟨ɡ⟩ and ⟨
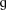 ⟩ do not match and if the first looks like a ⟨γ⟩, then you have an issue with your default font. See Rendering issues.
⟩ do not match and if the first looks like a ⟨γ⟩, then you have an issue with your default font. See Rendering issues.
- ↑ The IPA value of the letter ⟨j⟩ is counter-intuitive to many English speakers. However, it does occur with this sound in a few English words, such as hallelujah and Jägermeister.
- ↑ Although the IPA symbol [r] represents a trill, /r/ is widely used instead of /ɹ/ in broad transcriptions of English.
- ↑ The phoneme /hw/ is not distinguished from /w/ in the many dialects with the wine–whine merger, such as RP and most varieties of GenAm. For more information on this sound, see voiceless labio-velar approximant.
- ↑ A number of English words, such as genre and garage, are pronounced with either /ʒ/ or /dʒ/.
- ↑ In most dialects, /x/ is replaced by /k/ in most words, including loch. In ugh, however, it is often replaced by /ɡ/ (a spelling pronunciation), and in Chanukah by /h/
- ↑ In non-rhotic accents like RP, /r/ is not pronounced unless followed by a vowel. In some Wikipedia articles, /ɪər/ etc. may not be distinguished from /ɪr/ etc. When they are distinguished, the long vowels are sometimes transcribed /iːr/ etc. by analogy with vowels not followed by /r/. These should be fixed to correspond with the chart here.
- ↑ 8,0 8,1 8,2 8,3 8,4 Note that many speakers distinguish monosyllabic triphthongs with R and disyllabic realizations: hour /ˈaʊər/ from plougher /ˈplaʊ.ər/, hire /ˈhaɪər/ from higher /ˈhaɪ.ər/, loir /ˈlɔɪər/ from employer /ɨmˈplɔɪ.ər/, mare /ˈmɛər/ from player /ˈpleɪ.ər/.
- ↑ /ɒ/ is not distinguished from /ɑː/ in dialects with the father–bother merger such as GenAm.
- ↑ In some regions (including California), what would normally be [æŋ] is pronounced as [eŋ] or [eɪŋ], so that the "a" in "rang" is closer to the "ai" in "rain" than the "a" in "rag"
- ↑ Pronounced the same as /ɛr/ in accents with the Mary–marry–merry merger.
- ↑ Many speakers, for example in most of Canada and much of the United States, have a different vowel in price and ride. Generally, an [aɪ] is used at the ends of words and before voiced sounds, as in ride, file, fine, pie, while an [ʌɪ] is used before voiceless sounds, as in price and write. Because /t/ and /d/ are often conflated in the middle of words in these dialects, derivatives of these words, such as rider and writer, may be distinguished only by their vowel: [ˈɹʷaɪɾəɹ], [ˈɹʷʌɪɾəɹ]. However, even though the value of /aɪ/ is not predictable in some words, such as spider [ˈspʌɪɾəɹ],[navedi vir] dictionaries do not generally record it, so it has not been allocated a separate transcription here.
- ↑ 13,0 13,1 Transcribed as /e/ by many dictionaries.[1]
- ↑ Pronounced the same as /ɛr/ in accents with the Mary–marry–merry merger. Often transcribed as /eə/ by British dictionaries and as /er/ by American ones. The OED uses /ɛː/ for BrE and /ɛ(ə)r/ for AmE.[2]
- ↑ Same as /ɪr/ in accents with the mirror–nearer merger.
- ↑ /ɔː/ is not distinguished from /ɒ/ (except before /r/) in dialects with the cot–caught merger such as some varieties of GenAm.
- ↑ Commonly transcribed /əʊ/ or /oː/.
- ↑ /ɔər/ is not distinguished from /ɔr/ in dialects with the horse–hoarse merger, which include most dialects of modern English.
- ↑ /ʊər/ is not distinguished from /ɔr/ in dialects with the pour–poor merger, including many younger speakers.
- ↑ In dialects with yod dropping, /juː/ is pronounced the same as /uː/ after coronal consonants (/t/, /d/, /s/, /z/, /n/, /θ/, and /l/) in the same syllable, so that dew /djuː/ is pronounced the same as do /duː/. In dialects with yod coalescence, /tj/, /dj/, /sj/ and /zj/ are pronounced /tʃ/, /dʒ/, /ʃ/ and /ʒ/, so that the first syllable in Tuesday is pronounced the same as choose.
- ↑ This phoneme is not used in the northern half of England, some bordering parts of Wales, and some broad eastern Ireland accents. These words would take the ʊ vowel: there is no foot–strut split.
- ↑ 22,0 22,1 In some articles /ɜr/ is transcribed as /ɝː/, and /ər/ as /ɚ/, when not followed by a vowel.
- ↑ Pronounced [ə] in Australian and many US dialects, and [ɪ] in Received Pronunciation. Many speakers freely alternate between a reduced [ɪ̈] and a reduced [ə]. Many phoneticians (vd. Olive & Greenwood 1993:322) and the OED use the pseudo-IPA symbol ⟨
ɪ⟩ [3], and Merriam–Webster uses ⟨ə̇⟩. - ↑ Pronounced [ə] in many dialects, and [ɵw] or [əw] before another vowel, as in cooperate. Sometimes pronounced as a full /oʊ/, especially in careful speech. (Bolinger 1989) Usually transcribed as /ə(ʊ)/ (or similar ways of showing variation between /oʊ/ and /ə/) in British dictionaries.
- ↑ Pronounced [ʊ] in many dialects, [ə] in others. Many speakers freely alternate between a reduced [ʊ̈] and a reduced [ə]. The OED uses the pseudo-IPA symbol ⟨
ʊ⟩ [4]. - ↑ Pronounced [i(ː)] in dialects with the happy tensing, [ɪ] in other dialects. British convention used to transcribe it with ⟨ɪ⟩, but the OED and other influential dictionaries recently converted to ⟨i⟩.
- ↑ It is arguable that there is no phonemic distinction in English between primary and secondary stress (vd. Ladefoged 1993), but it is conventional to notate them as here.
- ↑ Full vowels following a stressed syllable, such as the ship in battleship, are marked with secondary stress in some dictionaries (Merriam-Webster), but not in others (the OED). Such syllables are not actually stressed.
- ↑ Syllables are indicated sparingly, where necessary to avoid confusion, for example to break up sequences of vowels (moai) or consonant clusters which an English speaker might misread as a digraph (Vancouveria, Windhoek).
Zunanje povezave
[uredi | uredi kodo]- Getting JAWS 6.1 to recognize "exotic" Unicode symbols—For help on getting the screen reader JAWS to read IPA symbols
- IPA TTS (text-to-speech) bookmarklet
